GIA Teaches You 4Cs - How To Choose Giamond
The most influential sparkle in 4C - Cut
Whether a diamond is dazzling or not depends on the cut of the diamond, so the cut controls the quality of the diamond. The diamond cutter will accurately calculate the most perfect cutting angle ratio according to the optical properties of the diamond, so that the diamond exhibits the best dispersion and brightness. Because only a perfect cut can perfectly present the visible fire, sparkle and brightness of the diamond to the viewer’s eyes, if the cut is not good, even if the diamond is the most transparent and colorless D color, the diamond will still be bleak and without brilliance. No beauty.

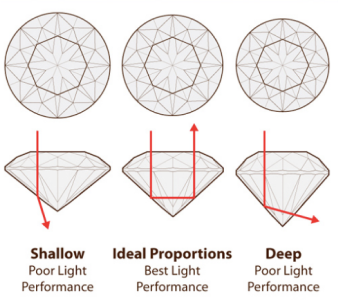
How the cut determines the fire, sparkle and brightness of a diamond?
Fire
The fire color of a diamond is like a flame. When the light hits the diamond facet, the dispersion caused by the different angle of refraction will disperse the white light into a rainbow color. The fire on the crown (surface) of the diamond , Determined by the ratio (Cut Grade) and the degree of symmetry (Symmetry).
Scintillation
When the diamond moves with the light and the eyes are obliquely observed at different angles, the flicker effect of the diamond due to the internal black and white contrast changes in the depth of the light on the facet. The best effect on the flicker is determined by the ratio (Cut Grade), Symmetry (Symmetry) is determined.
Brilliance
refers to the brightness of total internal reflection caused by the reflection of the crown facet and pavilion facet of the diamond surface, which is mainly determined by polishing (Polish) and proportion (Cut Grade).
Hearts and Arrows Ratio
The perfect overall ratio can show the hearts and arrows. This special optical effect, also known as Cupid Turner, is the most popular cutting technique for consumers, and it also makes a diamond more meaningful.

Proportion standard grade
The above grades are the comprehensive grades obtained by combining the angles and proportions of each part of the diamond. For the so-called "Excellent" diamond, all angles and ratios must be within the specified numerical range. If one of them does not match, it will be downgraded to the "Very Good" grade.
Cut Symmetry Polish
Various exquisite cut shapes(Shape)
Refers to the outer contour of the diamond cut. Round diamonds are the most popular cut shape because they can show total internal reflection and maximize the refractive index of the diamond. There are also some special shapes, such as emerald cut, pillow, oval, heart, radiant, marquise, princess, pear, etc. These shapes are also called special-shaped diamonds, and the price will be more favorable than round diamonds, and their unique beauty is deeply loved by the public.

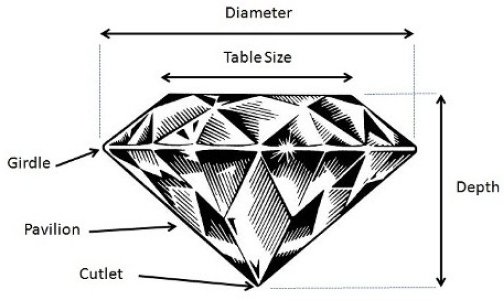
Diamond Anatomy
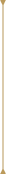
 Girdle
Girdle


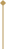 Culet
Culet
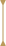 Crown
Crown
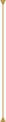 Pavilion
Pavilion
-
Diameter
Measure the straight line length from one girdle to the other girdle of the diamond
-
Table
The top of the diamond, which extends from the girdle to the table top, mainly refracts colored light
-
Depth
The height measured from the tip of the gemstone to the table top
-
Crown
education.cutText26.1
-
Pavilion
The bottom of the diamond extends from the girdle to the tip
-
Culet
It's the tip of the gem. "None" or "Small" is better
-
Girdle
The border between the crown and the pavilion lays the diamond's circumference and the position of the GIA laser number
Symmetry
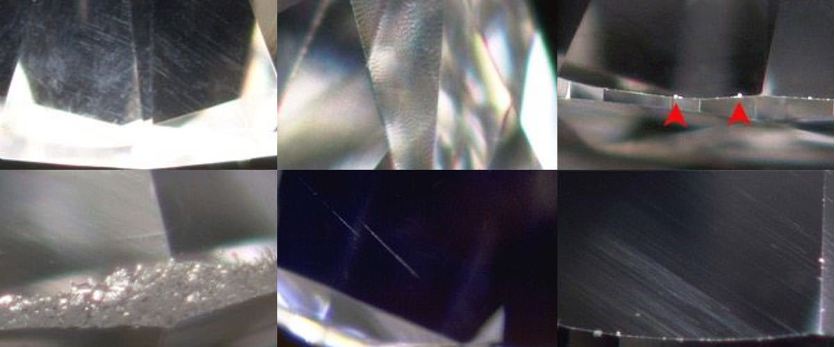
Symmetry refers to whether the facets of the diamond are aligned and whether the table is symmetrical as a whole. If the facets of the diamond are asymmetrical, for example, the lower waist facet overlaps the tabletop kite surface, the bottom tip is off-center, and the waist facet is too thick or thin. …And so on, it will affect the optical refraction of the light in the diamond, the hearts and arrows that come out will be a bit skewed and not neat and beautiful, and the overall fire and sparkle will have a great impact, and it is the first in the cut evaluation. Secondly, it is better to choose Very Good-Excellent at least.

Polish
Polishing refers to the smoothness of the diamond surface polishing, the polishing traces during polishing, and whether the facets and edge positions of the diamond are polished neatly and sharply. It is the surface flatness of the diamond. The polishing traces are almost invisible to the naked eye. Quality affects the brightness of the diamond, but does not have a great effect on the overall fire and sparkle, so the Good-Excellen grade can be considered.